In modern power systems, current transformers (CTs) are a vital measurement and protection device. They are widely used in current monitoring, protection equipment, metering systems, and automation control in the power industry by converting high currents into lower, measurable standard currents. With the development of smart grids, current transformers are becoming more and more widely used. They are not only the "eyes" of the power system, but also the "guardian" to ensure the stable operation of the system.
Basic Principles of Current Transformer
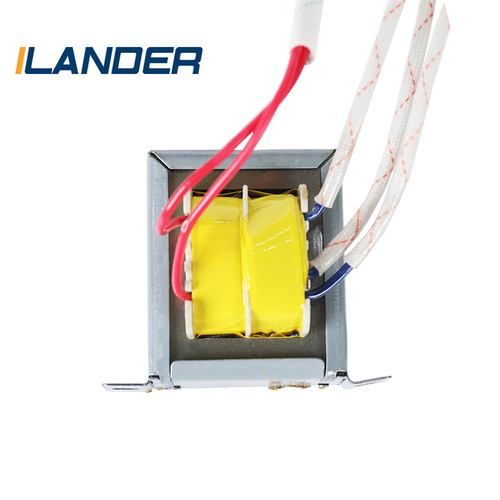
The working principle of the current transformer is based on the electromagnetic induction method. It measures the current of the high-current main circuit and converts it proportionally into a low-current secondary circuit output. Usually, the current transformer consists of a primary winding, an iron core, and a secondary winding. The primary winding is connected in series with the main power circuit, and the secondary winding is connected to the measuring instrument or protection device.
When the current in the main circuit passes through the primary winding, the magnetic field generated induces current in the iron core. The magnetic field of the iron core is proportional to the main circuit current, and then transmits a low-current output signal through the secondary winding. The secondary current is usually a few hundredths of the primary current, which makes the current transformer a key tool for accurately measuring large currents.

Main classification of current transformers
Depending on the design, use occasion and function, current transformers can be divided into the following types:
Classification by purpose
Measuring current transformer: mainly used for current measurement and monitoring, commonly used in metering, protection equipment and current sensors.
Protective current transformer: used for power system protection, can quickly respond to current abnormalities (such as short circuit, overload, etc.), disconnect the circuit in time, and ensure equipment safety.
Classification by structure
Open current transformer: with an openable core, it can be easily installed and disassembled, suitable for on-site installation and maintenance.
Closed current transformer: the core is closed, suitable for long-term stable working environment, usually used in fixed equipment.
Classification by measurement range
Low voltage current transformer: suitable for low voltage power system, usually rated voltage below 1000V.
High voltage current transformer: used for high voltage power system, rated voltage can reach 35kV and above.
Application fields of current transformers
Current transformers are widely used and are an indispensable component of power systems. Its main application fields include:
Measurement and monitoring of power systems
In power systems, current transformers are used to monitor the size of current in real time and provide accurate measurement data for power metering. It helps power companies accurately measure user power consumption by providing standard current signals.
Power equipment protection
Current transformers are one of the core components of protection devices. When current abnormalities (such as short circuits and overloads) occur, current transformers can quickly transmit current change signals, triggering protection devices to cut off power supply, and prevent equipment damage or fire and other dangerous events.

Automation control systems
In smart grids and automation systems, current transformers work with PLCs (programmable logic controllers) and other control devices to monitor current status and adjust loads in real time, optimizing the operating efficiency of the power grid.
Health diagnosis and maintenance of power equipment
By regularly detecting the output signal of the current transformer, the working status of the power equipment can be understood in real time, and preventive maintenance can be performed to extend the service life of the equipment.
Advantages of current transformers
Advantages:
High-precision measurement: Current transformers can provide accurate current signals to ensure the reliability of power metering and equipment protection.
High safety: Since its working principle is to convert high current into low current signals, it avoids the safety risks of direct contact with high current circuits.
Good stability: The design structure of the current transformer is simple and stable, and it can work stably for a long time.
Strong adaptability: It is suitable for different power systems, whether it is high voltage, low voltage, or dynamic and static load environments.
As one of the core devices in the power system, the current transformer plays a vital role. It not only plays the role of "eyes" and "guardian" in the measurement, monitoring and protection of the power system, but also demonstrates its irreplaceable value in the development of smart grids. With the continuous advancement of technology and the diversification of application needs, current transformers will continue to play an important role in the future power industry.
 English
English Español
Español