In modern power systems, power transformers are known as the "heart of energy flow". Whether it is a power plant, a substation, or a large industrial park, it is inseparable from its stable output and efficient transmission. With the development of new energy and smart grids, higher requirements are placed on the performance, safety and intelligence level of power transformers.
1. What is a power transformer? ——The bridge of voltage regulation
A power transformer is an electrical device that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to convert AC power of a certain voltage level into AC power of another voltage level. It is mainly used to increase or decrease voltage, to minimize energy loss during long-distance transmission of electricity, and to meet the voltage requirements of power terminal equipment.
In a complete power transmission and distribution system, it usually includes:
Step-up transformer at the generating end
Relay transformer in the middle of the transmission line
Step-down transformer at the user side
II. Core structure analysis: the basis for building efficient energy conversion

The basic structure of the power transformer mainly includes the following core parts:
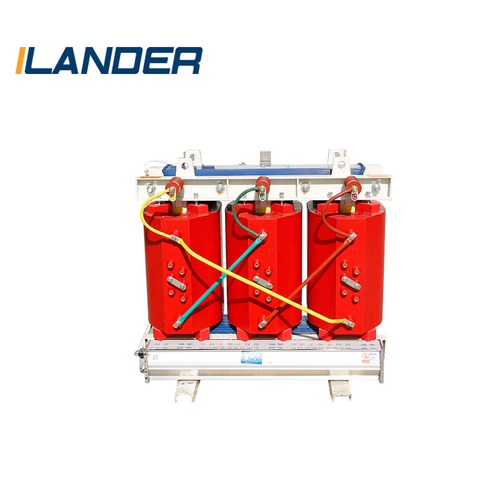
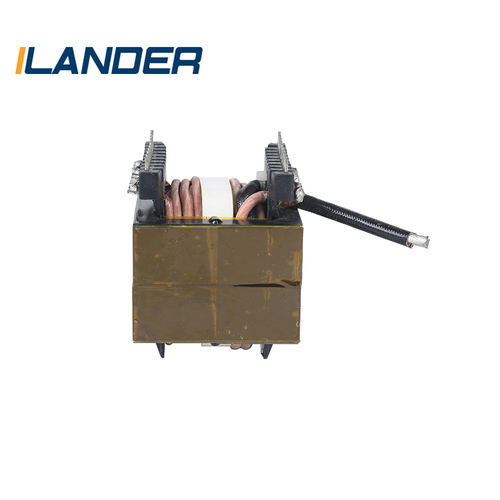
1. Core
The core is the magnetic circuit part of the transformer, which is generally made of highly magnetic silicon steel sheets stacked together. Its function is to conduct magnetic flux and reduce iron loss. Common structures include core type and shell type.
2. Winding
The winding is usually wound with copper or aluminum wires, divided into high-voltage windings and low-voltage windings, and is the carrier for electromagnetic induction energy conversion of the transformer.
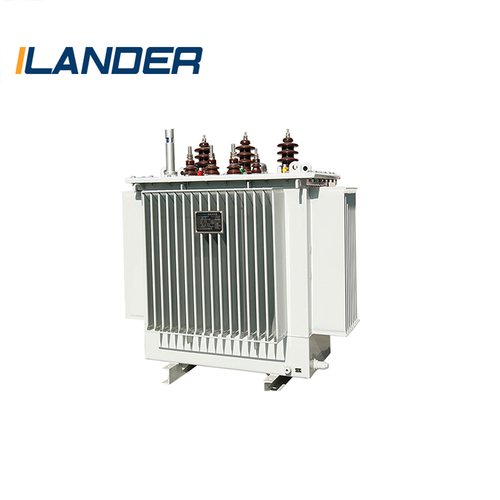
3. Oil tank and insulating oil (Transformer Oil)
Traditional transformers generally use transformer oil as a cooling and insulating medium. The oil tank not only protects the internal components, but also plays a role in heat dissipation and insulation.
4. Insulation system and cooling system
High-quality insulating paper, paperboard, and resin materials can effectively prevent breakdown between windings and between windings and cores. There are many forms of cooling systems, such as oil cooling, self-cooling, air cooling, and water cooling.
3. Common types of classification: diverse choices to meet the needs of multiple scenarios
1. Classification by structural form
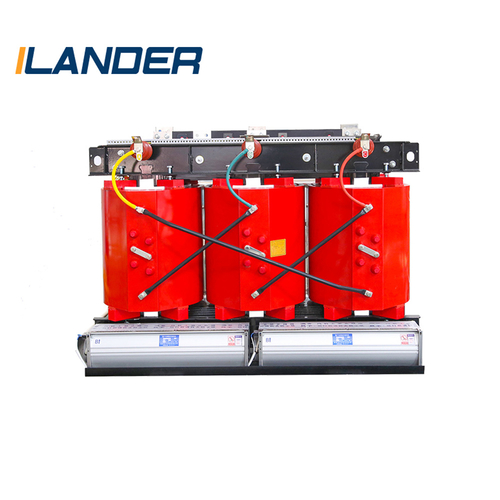
Oil-immersed transformer: good heat dissipation performance, suitable for large power grids.
Dry-type transformer: oil-free design, environmentally friendly and safe, suitable for indoor or fire-resistant places.
2. Classification by number of phases
Single-phase transformer: used for small equipment or rural power grids.
Three-phase transformer: the most widely used, suitable for industrial and urban power systems.
3. Special function type
Autotransformer: saves materials, high efficiency, but poor isolation performance.
Voltage regulating transformer: has adjustable output voltage function, suitable for industrial scenarios that require voltage stability.
4. Typical application scenarios of power transformers

Urban power distribution system
The role of power transformers in urban residential and commercial buildings is particularly critical. It can convert high-voltage transmission power into low-voltage power supply to ensure residents' daily electricity use.
Industrial power field
Large-scale industrial equipment has extremely high requirements for voltage stability. Power transformers ensure that the equipment operates at a safe voltage for a long time to avoid losses and risks caused by voltage fluctuations.
New energy field
In wind power, photovoltaic and other new energy power stations, transformers can increase the output voltage, making it easier to access the national power grid and transmit over long distances.
Power transformers are not only a tool for power conversion, but also a guarantee for the stable operation of the entire energy system. From traditional power transmission to today's green smart grid, it has always played a key role. In the future, with the deep integration of AI technology, the Internet of Things and renewable energy, the "smartness" of power transformers will bring unlimited possibilities for the transformation of the global energy structure.
 English
English Español
Español